Download Resource
Download Resource
Download Resource
Download Resource
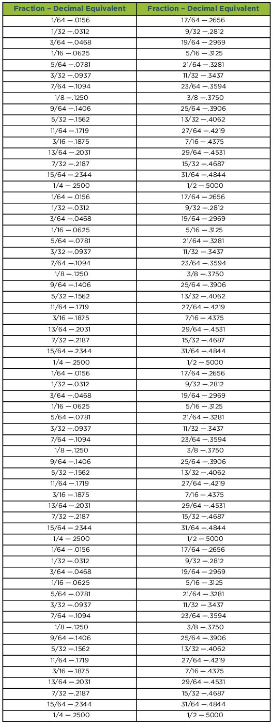
Download Resource
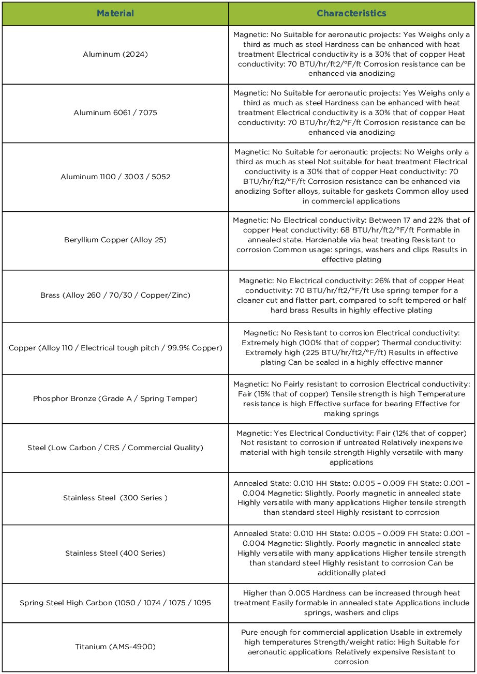
Download Resource
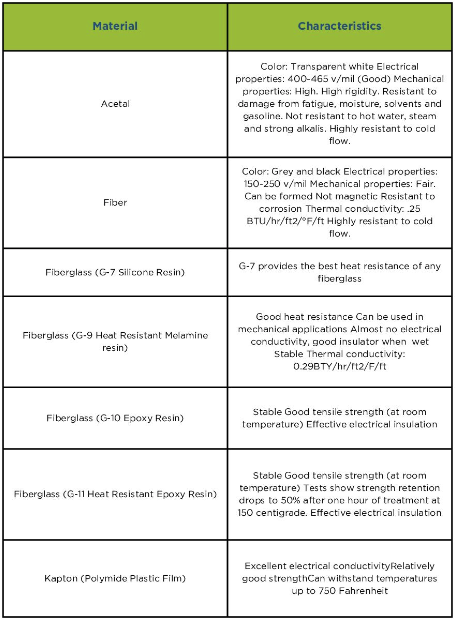
Download Resource
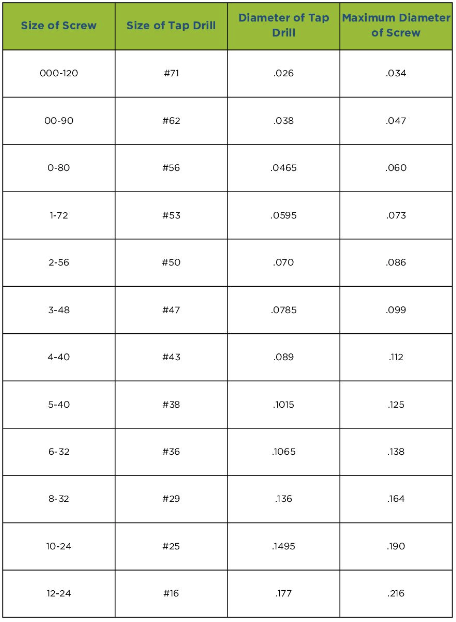
Download Resource
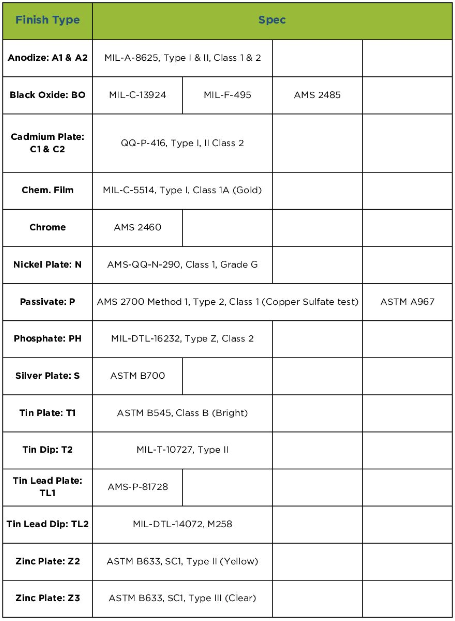
Download Resource
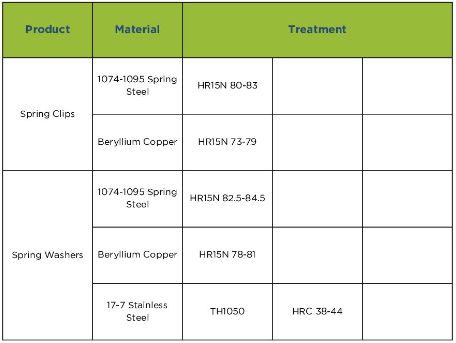
Download Resource
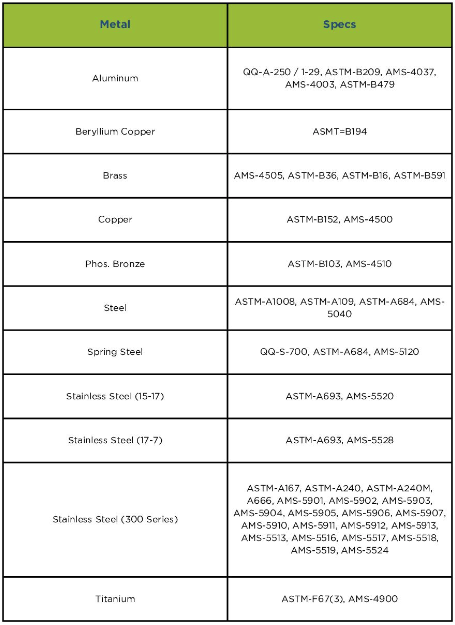
Download Resource
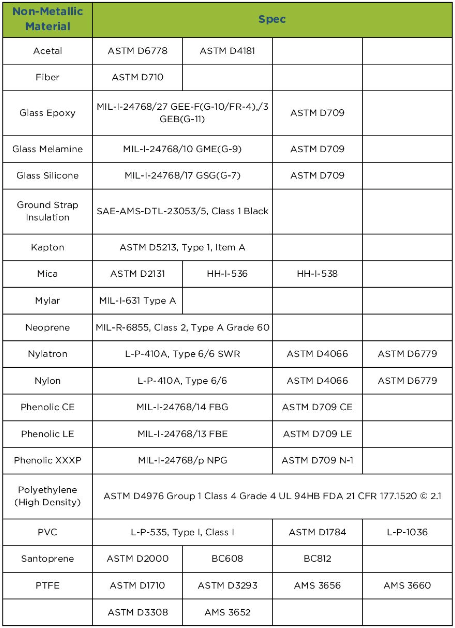
Download Resource
